The term “diamond tester” in the world of jewellery often generates interest and confusion. Many people wonder if they really work. To uncover the truth behind these questions, let’s explore the details of diamond testers.
Understanding Diamond Testers
Diamond testers are devices designed to distinguish diamonds from their most common imitations, such as cubic zirconia (CZ) and moissanite. These instruments were first introduced in the early 1980s and primarily used thermal conductivity to differentiate diamonds from CZ. This method proved effective however, with the emergence of moissanite in the late 90s, which has thermal conductivity similar to that of diamond, traditional diamond testing methods were challenged.
In response to the moissanite challenge, the jewellery industry shifted towards testers that rely on electrical conductivity. Unlike diamonds, moissanite exhibits electronic conductivity, which offers a unique characteristic for differentiation. Although these advancements have improved testing accuracy, some exceptions still exist. For instance, natural blue diamonds, such as the famous Hope Diamond, can produce “moissanite” results due to their electrical conductivity. Additionally, many lab-grown diamonds exhibit similar traits, further complicating testing outcomes.
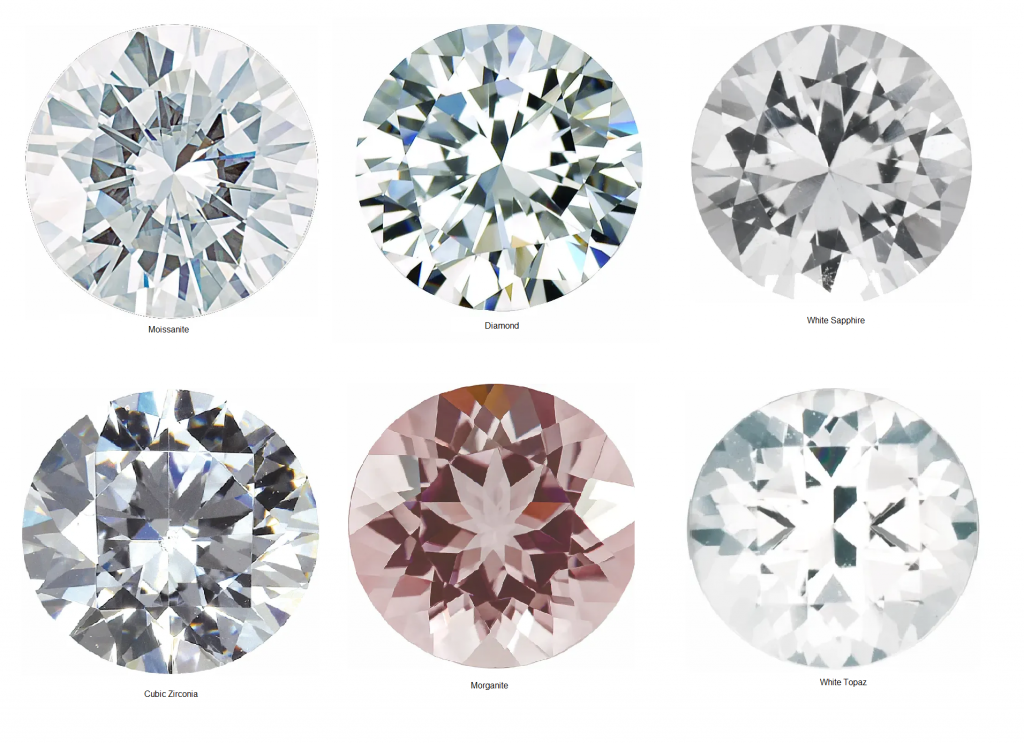

Lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical and physical properties as natural diamonds, making it difficult to differentiate between them. Traditional diamond testers may not be able to distinguish between the two since lab-grown diamonds often have electrical conductivity similar to moissanite. However, reputable certification and laser inscriptions can help verify the authenticity of lab-grown diamonds. Furthermore, advancements in testing technology are ongoing to overcome the challenges posed by evolving diamond synthesis techniques.
In addition to lab-grown diamonds, the world of diamond testing is further complicated by simulants and imitations. Simulants are gems that look like diamonds but have different physical and chemical properties. They can be natural gems such as white sapphire or human-made materials like CZ and moissanite. These imitations are sold under different names, which further adds to the complexity.
Using Diamond Testers
In recent times, there has been a growing trend on TikTok that has caused a lot of confusion and upset. Some TikTok videos show individuals using diamond testers to determine whether a stone is a real diamond or not. However, this method of testing is not always reliable and can lead to suspicion and mistrust.
To address this issue, YouTuber By Bonnie Jewelry recently released a video where she invites a gemmologist to provide expert insights on the matter. The video aims to clear up any confusion and provide accurate information on identifying diamonds.
It’s important to note that using a diamond tester is not always a foolproof method for testing diamonds, as many factors can affect the results. Some stones may give a false positive or false negative result, leading to confusion and unnecessary anxiety. Therefore, consulting with trained professionals is crucial for customers to get an accurate assessment of a diamond’s authenticity.
The major issue with these traditional diamond testers is their reliance on outdated technology. With advancements in lab-created diamonds, these testers struggle to keep pace. As a result, lab-grown diamonds are often misidentified as moissanite due to their shared electrical conductivity traits.
Moissanite is a popular alternative to diamonds due to its affordability and similar appearance. The misidentification of lab-grown diamonds as moissanite can lead to confusion and financial loss for both buyers and sellers. To overcome this issue, newer and more advanced diamond testers have been introduced that use advanced technology to accurately identify diamonds, including lab-grown diamonds. These testers make use of advanced techniques such as UV spectrometry, thermal conductivity, and photoluminescence to accurately distinguish between diamonds and other gemstones.
By Bonnie Jewelry’s video offers a firsthand demonstration of diamond testers, showcasing their reliance on assessing a stone’s thermal or electrical conductivity. However, conventional testers, like the one featured, falter in accurately discerning lab-grown diamonds.
Bonnie then showcases the groundbreaking technology for testing diamonds—the Raman spectrometer. This advanced instrument brings diamond lovers peace of mind as it generates diagnostic spectra that go beyond the constraints of conventional testers. The Raman spectrometer is specifically designed to differentiate between diamonds, moissanite, and CZ with accuracy, making it an invaluable tool for jewellery experts.
The Raman spectrometer is a highly advanced device that can analyse diamonds in unprecedented detail. It employs a cutting-edge technology that uses a laser to excite the atoms in the diamond, causing them to emit light at specific frequencies. This light is then analysed by the Raman spectrometer, which produces a spectrum that is unique to that diamond. The spectrum is then compared to a vast database of known spectra to identify the diamond with incredible accuracy.
By Bonnie Jewelry’s video has revealed the significance of educating customers about the limitations of conventional diamond testers and the advancements in testing technology. By imparting knowledge to the customers, you can reduce the probability of receiving complaints from those who have used outdated testers. Diamond professionals are responsible for communicating transparently and ensuring that customers feel confident and assured in their purchases. Prioritising education helps build trust and strengthens relationships, which in turn enhances the integrity of the trade.